Introduction
In a career with over 25 years of software innovation, I have often found myself at the crossroads of technology and Intellectual Property (IP) law. My collaborations with industry heavyweights like GE and Apple, along with numerous co-development ventures, have navigated me through the intricate maze of patent processing. Although the journey has been rewarding, the lengthy and often convoluted patent process is a narrative many innovators can resonate with. This narrative raises a compelling question: Can the patent process be simplified and strengthened to foster innovation rather than stifle it? Enter Explainable AI (XAI), a promising horizon that beckons a simplified and more accessible patent process for legal professionals and tech innovators.
Explaining XAI and Intellectual Property
Explaining XAI and its distinction from traditional AI is essential for understanding its potential in patent law. Unlike traditional AI, which operates as a “black box,” XAI provides a transparent window into its workings, explaining the rationale behind its conclusions. This transparency is pivotal in legal settings where understanding the basis of decisions is imperative. Intellectual Property, on the other hand, is a realm that protects creations of the mind, such as inventions, literary and artistic works, designs, and more. Patents, a form of IP protection, grant the patent holder exclusive rights to an invention, shielding their innovation from being used or sold by others.
The Traditional Patent Process
The traditional patent process is a meticulous venture involving numerous stages from conception to grant. It necessitates a thorough analysis to ensure the novelty and legality of an invention, which is time-consuming and often taxing for innovators. The complexity escalates with the voluminous legal texts and existing patents that need to be reviewed to ascertain the uniqueness of the new invention. Here is a relatively simple patent and a more complex one. Both took several years to be awarded.
XAI and Streamlined Patent Processing
The advent of XAI heralds a new era of streamlined patent processing. By automating the analysis of existing patents and legal texts, XAI accelerates the preliminary stages of patent acquisition. It can sift through vast datasets, identifying potential overlaps or issues with the proposed patent and providing a transparent rationale for its findings. Furthermore, XAI’s ability to offer understandable insights and recommendations emerges as a boon for decision-making. For instance, an XAI system could rapidly analyze a proposed patent against a database of existing patents, highlighting any potential overlaps or issues thereby aiding in quicker resolutions. Here is the flow of the traditional patent process vs using XAI’s.
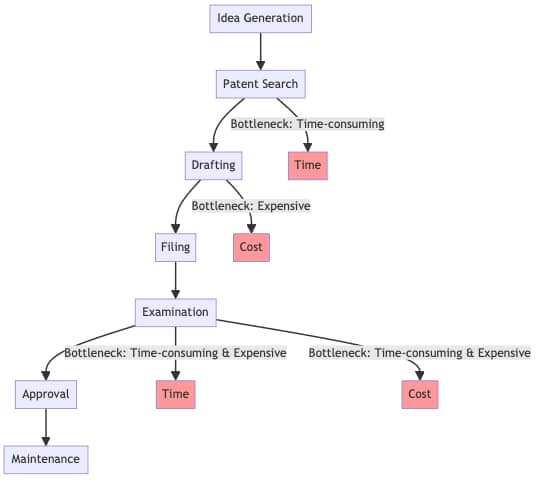
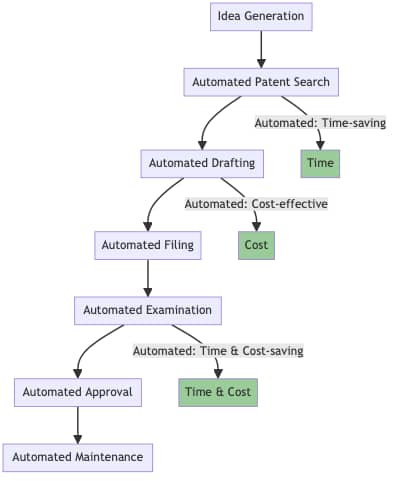
Automated Patent Process using XAI
- Idea Generation
- AI algorithms can help identify gaps in existing patents and suggest areas where new inventions could be valuable.
- Patent Search
- XAI can quickly scan existing patents and academic papers to identify similar inventions. This saves time and ensures a more comprehensive search.
- Drafting
- Natural Language Generation (NLG) tools can assist in drafting the patent application, making it more cost-effective.
- Filing
- The filing process can be automated to populate and submit forms, reducing manual errors and saving time.
- Examination
- XAI can pre-assess the patent application against criteria used in manual examinations, flagging any potential issues for quick resolution.
- Approval
- Once the application passes the automated examination, the approval process can be expedited.
- Maintenance
- Reminders and auto-renewal features can be set up for patent maintenance fees and other recurring tasks.
By automating these stages, the patent process becomes more efficient, cost-effective, and less prone to human error.
Real-World Implications
The real-world implications of XAI in patent processing are beginning to surface, albeit gradually. Legal tech firms are developing AI tools to automate patent analysis, which could significantly reduce the time and resources spent on preliminary patent examination.
There are several AI-powered tools available that facilitate automated patent analysis to assess the novelty and other aspects of inventions. These tools can significantly speed up the patent research process by analyzing existing patents and other related documents. Here are some notable AI tools that are being utilized to automate patent analysis:
- PatentSight:
- PatentSight is an AI-driven analytics platform specializing in in-depth patent portfolio analysis.
- It provides visualizations of patent landscapes, identifies potential acquisition targets, and assesses the value of patents.
- Cipher:
- Cipher utilizes AI and machine learning to analyze patent data.
- It offers competitive analysis, technology trend tracking, and patent valuation.
- Relecura:
- Relecura is a comprehensive patent analytics tool that combines AI and visualization.
- It aids users in navigating patent landscapes, identifying emerging technologies, and assessing the competitive landscape.
- Clarivate Analytics (formerly Derwent):
- This platform offers AI-driven patent analysis tools, including PatentSight and Derwent Innovation, which assist in patent valuation, portfolio management, and competitive intelligence.
- IP.com:
- IP.com provides AI-powered solutions for patent search and analysis.
- It offers features such as semantic search, patent landscaping, and competitor tracking.
- PatSeer:
- PatSeer is an AI-driven patent research platform with integrated analytics, project workflows, and collaboration capabilities, trusted by over 6000+ professionals globally.
- USPTO’s AI Prototype:
- In 2021, the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office developed an AI-based prototype search system for use by examiners during examinations.
Getting Started with XAI
Embarking on the XAI journey may seem daunting, especially in a field as nuanced as patent law. However, there are several resources and platforms available to ease this transition. Tools like LIME (Local Interpretable Model-agnostic Explanations) and SHAP (SHapley Additive exPlanations) provide a good starting point for implementing XAI. These tools are renowned for making AI and machine learning models more interpretable by providing clear, understandable explanations for the decisions these models make.
While the potential of XAI is promising, it’s imperative to acknowledge the hurdles. Data privacy, the accuracy of AI analysis, and the necessity of human oversight are among the considerations that need careful deliberation. Ensuring a balanced approach that values ethical considerations alongside technological advancements is crucial for successfully integrating XAI into legal practices.
The Promising Frontier
The marriage of Explainable AI and Intellectual Property law heralds a promising frontier in simplifying the patent process. The collaborative potential between legal professionals and tech innovators could drive a new wave of legal tech that makes patent processing more accessible, transparent, and efficient. As we venture into this uncharted territory, fostering a dialogue between the legal and tech sectors and exploring the capabilities of XAI is essential for harnessing the full potential of this innovative intersection. Consider the following use cases:
- Collaborative Patent Review:
- Legal professionals and tech innovators could collaboratively use XAI to review patent applications. XAI can automate the preliminary analysis, providing understandable insights on the novelty and patentability, while legal experts ensure compliance with IP laws.
- Transparent Patent Processing:
- XAI could provide a transparent platform for stakeholders to understand the stages and decisions in the patent process. Its explainable nature offers clarity on automated decisions, facilitating a more accessible and transparent patent processing experience.
- Prior Art Search:
- Utilizing XAI to perform comprehensive prior art searches, with the system explaining its reasoning, makes it easier for legal professionals to evaluate the relevance and thoroughness of the investigation. By employing XAI for automated prior art searches, inventors can quickly ascertain the novelty of their invention without waiting for legal feedback. The explainable nature of XAI can provide clear insights into how the system arrived at its conclusions, enabling inventors to understand the landscape of existing patents and make informed decisions early in the invention process, thus saving both time and resources. This streamlined approach can significantly expedite the initial stages of the patenting process and reduce the workload for legal professionals.
- Patent Drafting:
- An interactive platform powered by XAI could assist inventors and legal professionals in drafting patent applications by providing real-time feedback and explanations on claim scope, potential prior art conflicts, and compliance with patent laws, ensuring a well-articulated and compliant patent application.
Additional Resources and Next Steps
The journey doesn’t end here. Delving into platforms like Udemy, Coursera, or edX can provide access to courses on Explainable AI. Additionally, joining legal tech communities and forums can offer insights and connections in this evolving field. For the tech-savvy, exploring open-source XAI libraries and tools can provide a hands-on understanding of the technology and its application in legal settings.
Conclusion
The narrative seeks to shed light on the potential of XAI in transforming the patent process, making it more accessible, transparent, and efficient. It beckons a promising future where the power of Explainable AI catalyzes the collaborative efforts of legal professionals and tech innovators. The dialogue between these sectors, coupled with a deeper exploration and understanding of XAI, holds the key to unlocking a new era of legal tech that could redefine the landscape of patent processing and Intellectual Property law.

